Of stem cells, what would Gandhi say?
By Pankaj Mishra The New York Times MONDAY, AUGUST 22, 2005
In 2001, President George W. Bush restricted U.S. federal financing for stem cell research. The decision, which was shaped at least partly by the Republican Party's evangelical Christian base, and which disappointed many American scientists and businessmen, provoked joy in India.
The weekly newsmagazine India Today, read mostly by the country's ambitious middle class, spoke of a "new pot of gold" for Indian science and businesses. "If Indians are smart," the magazine said, American qualms about stem cell research "can open an opportunity to march ahead."
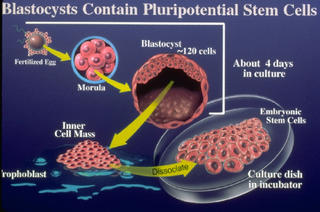
Just four years later, this seems to have occurred. According to Ernst & Young's Global Biotechnology Report in 2004, Indian biotechnology companies are expected to grow tenfold in the next five years, creating more than a million jobs. With more than 10,000 highly trained and cheaply available scientists, the country is one of the leading biotechnology powers along with Korea, Singapore, China, Japan, Sweden, Britain and Israel.
A top Indian corporation, the Reliance Group, owns Reliance Life Sciences, which is trying to devise new treatments for diabetes and Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases, and create human skin, blood and replacement organs genetically matched to their intended recipients.
Some scientists have even more ambitious ideas. Encouraged by the cloning of a sheep by British scientists in 1996, they plan to do the same with endangered species of Indian lions and cheetahs.
American scientists and businessmen note enviously that religious and moral considerations do not seem to inhibit Indian biotechnologists. But this indifference to ethical issues would have certainly appalled Gandhi, father of the Indian nation. Gandhi accused Western medicine, along with much of modern science and technology, of inflicting violence upon human nature. His vegetarianism and belief in nonviolence were derived from Indian traditions, mainly Hinduism, which is also the faith, though loosely defined, of most Indian scientists and businessmen.
Indeed, most evangelical Christians, who believe that the embryo is a person, may find more support in ancient Hindu texts than in the Bible. Many Hindus see the soul - the true Self (or atman) - as the spiritual and imperishable component of human personality.
After death destroys the body, the soul soon finds a new temporal home. Thus, for Hindus as much as for Catholics, life begins at conception.
The ancient system of Indian medicine known as Ayurveda assumes that fetuses are alive and conscious when it prescribes a particular mental and spiritual regimen to pregnant women. This same assumption is implicit in "The Mahabharata," the Hindu epic about a fratricidal war apparently fought in the first millennium B.C.
In one of its famous stories, the warrior Arjuna describes to his pregnant wife a seven-stage military strategy. His yet-to-be-born son Abhimanyu is listening, too. But as Arjuna describes the seventh and last stage, his wife falls asleep, presumably out of boredom. Years later, while fighting his father's cousins, the hundred Kaurava brothers, Abhimanyu uses well the military training he has learned in his mother's womb, until the seventh stage, where he falters and is killed.
But the religions and traditions we know as Hinduism are less monolithic and more diverse than Islam and Christianity; they can yield contradictory arguments. Early in "The Mahabharata," there is a story about how the hundred Kaurava brothers came into being. Their mother had produced a mass of flesh after two years of pregnancy. But then a sage divided the flesh into 100 parts, which were treated with herbs and ghee, and kept in pots for two years - from which the Kaurava brothers emerged.
Indian proponents of stem-cell research often offer this story as an early instance of human cloning through stem cells extracted from human embryos. They do not mention that "The Mahabharata" presents the birth of the hundred Kaurava brothers as an ominous event.
In any case, biotechnology may offer only pseudo-answers to many of India's urgent problems. For one thing, if and when lions and cheetahs emerge from biotechnology labs, the steadily deforested Indian countryside may not have a place for them. Stem cell research is also expensive, and seems glaringly so in a country which does not provide basic health care for most of its people. The advanced treatments promised by biotechnology are likely to benefit the rich, at least for the first few years.
In the meantime, the poor may be asked to offer themselves as guinea pigs. In an article on biotechnology last year, India Today asserted: "India has another gold mine - the world's largest population of 'naïve' sick patients, on whom no medicine has ever been tried. India's distinct communities and large families are ideal subjects for genetic and clinical research."
Scientism has few detractors in India; and the elites find it easy to propose technological rather than political and moral solutions to the problems of poverty, inequality and environmental damage.
Obsessed with imitating Western consumer lifestyles, most middle-class Indians are unlikely to have much time for Gandhi's belief that "civilization consists not in the multiplication of wants but in the deliberate and voluntary reduction of wants." They subscribe to a worldly form of Hinduism - one that now proves to be infinitely adjustable to the modern era, endorsing nuclear bombs and biotechnology as well as India's claim to be taken seriously as an emerging economic and scientific superpower.
Pankaj Mishra, an Indian novelist and journalist, is the author, most recently, of "An End to Suffering: The Buddha in the World." He lives in London and India.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home